Install pgAudit in your AWS RDS instance
Basic setup
First we’ll have to create an AWS RDS DB for this. We’ll use minimal permissions for this setup so that we can easily understand what’s going on.
Step 1: Create Database
Create your AWS account. Go to AWS RDS tab and click on “Create Database”
Step 2: Select Database
Standard create and postgreSQL
Select pg Version to the latest
And use free tier for now
Step 3: Add credentials
Username: postgres MasterPassword: postgres
For now.
Step 4: Allocate storage
Allocate the minimum possible storage for now
Step 5: Network
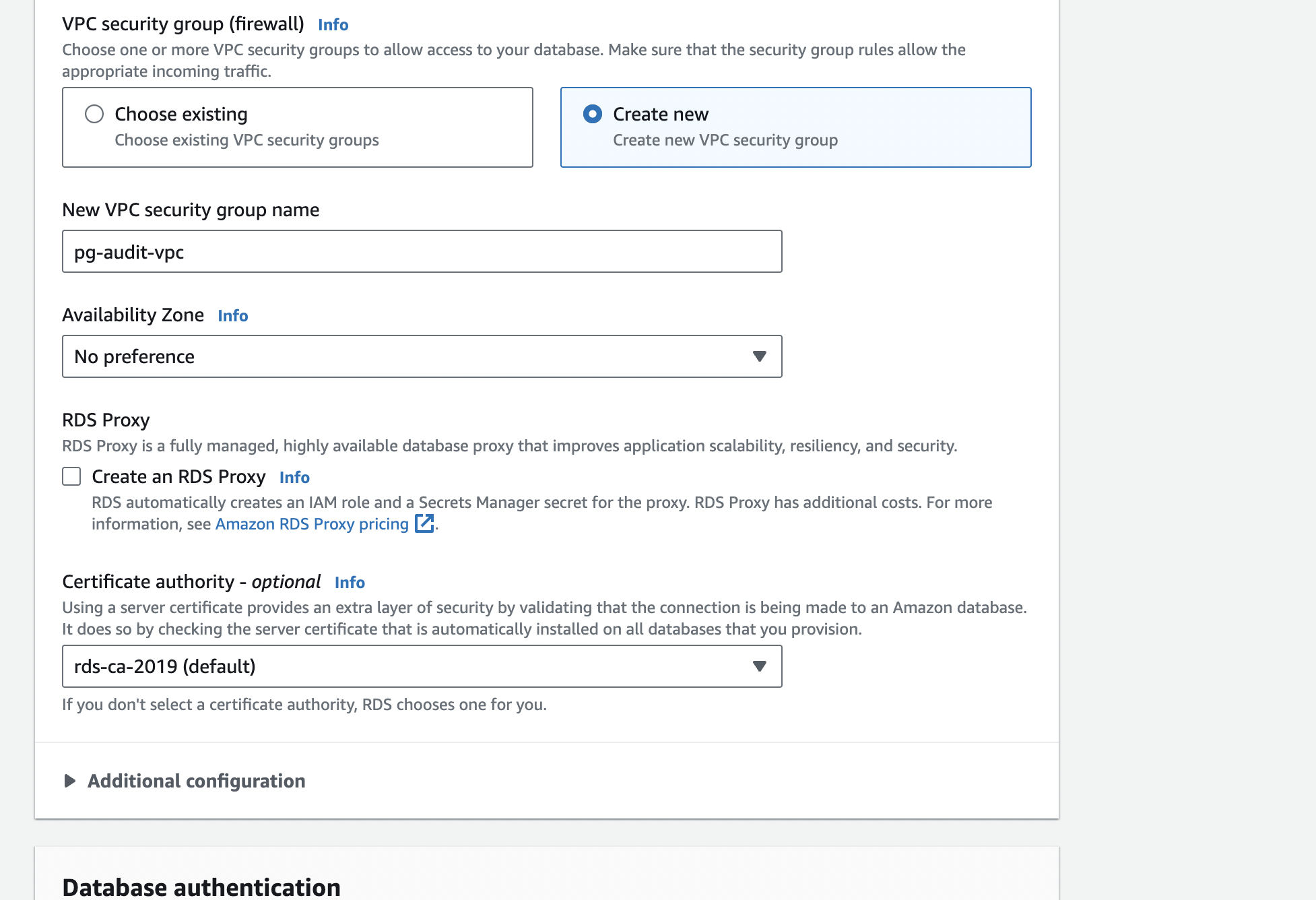
Create a new VPC for this RDS DB and create new security groups. Make ssure that they allow all traffic for now. Let’s improve the security later
Step 6: Set public access
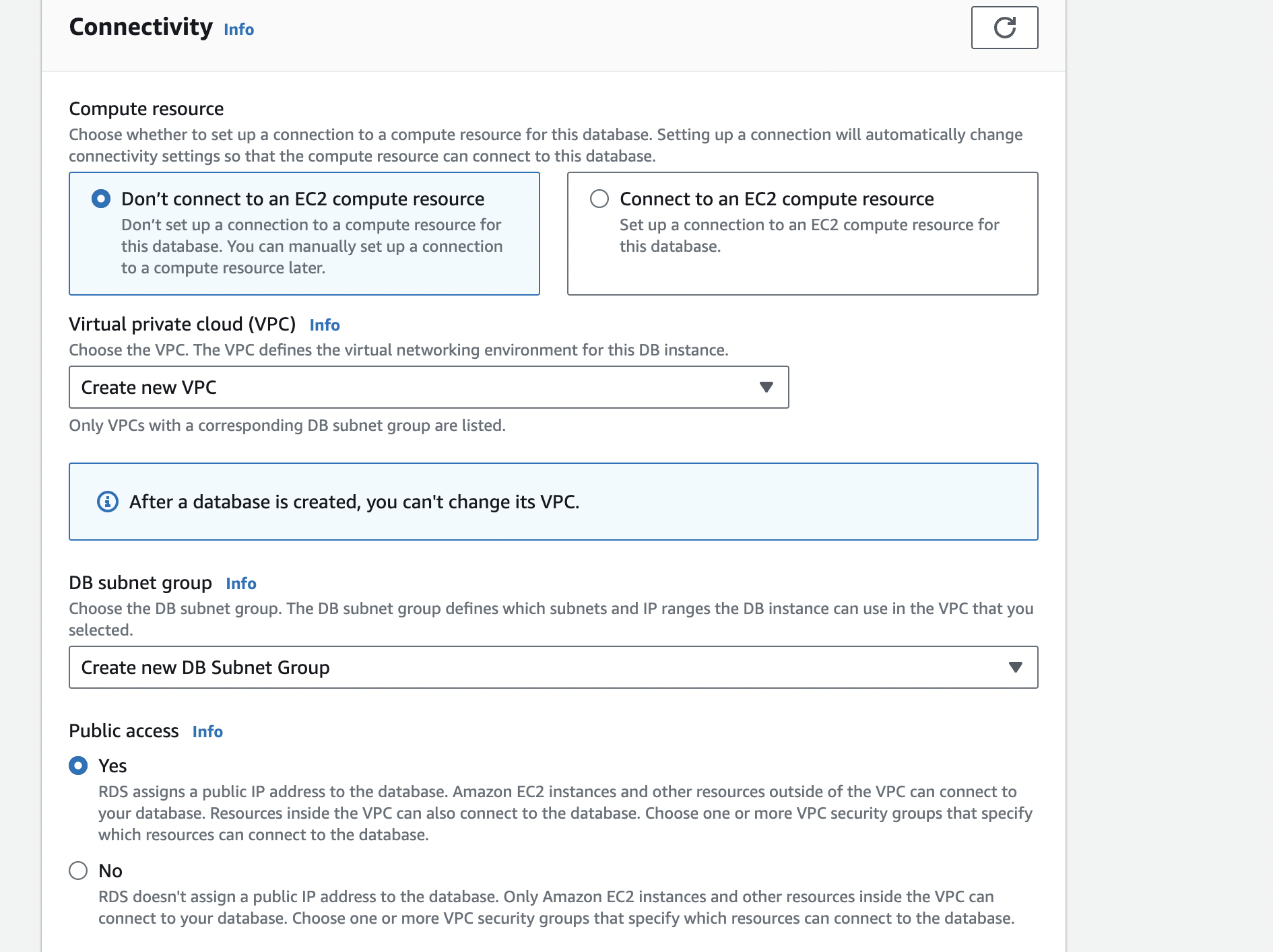
Remember to set Public access to true since we want to login from psql.
Step 7: DB Parameter group
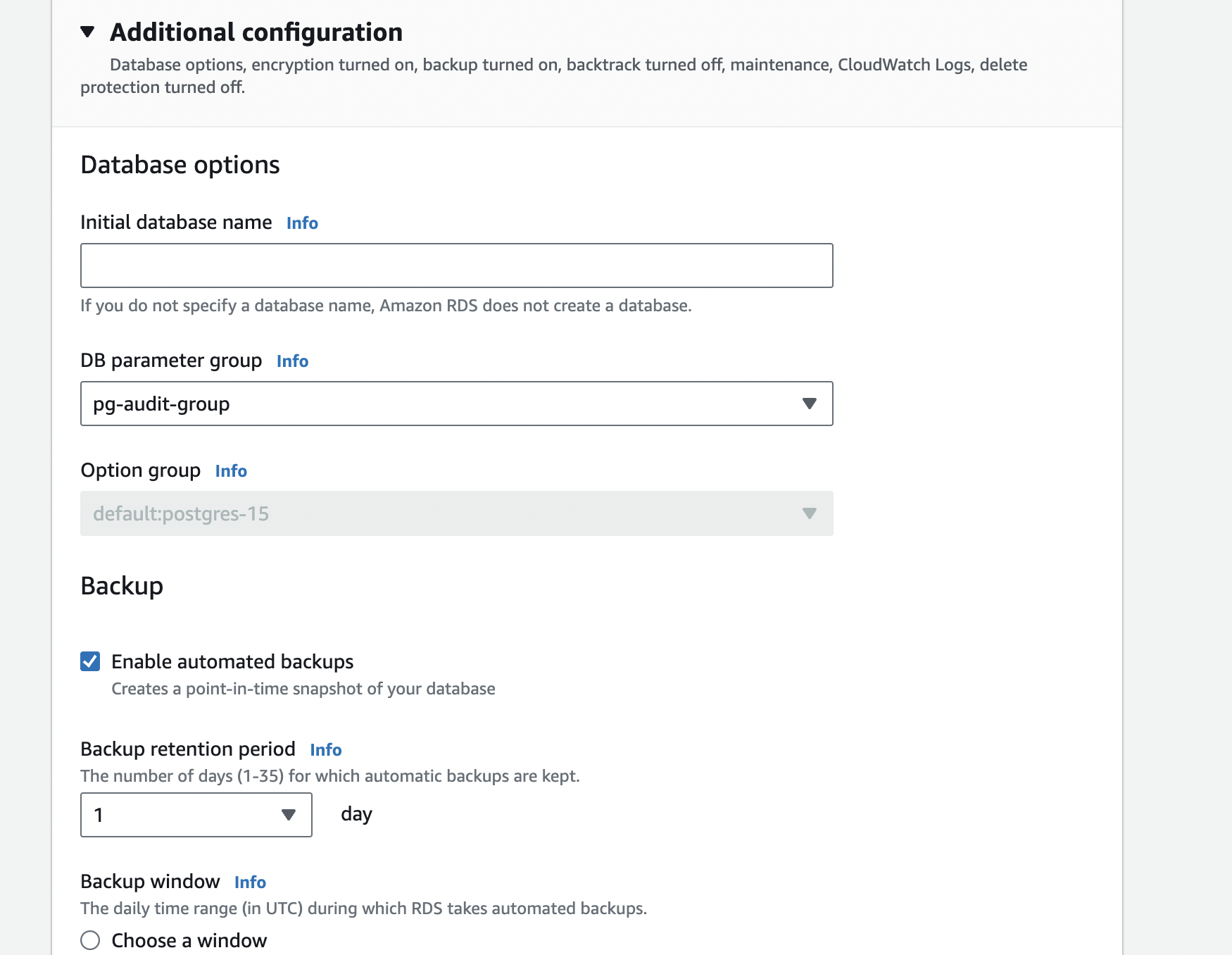
Remember the DB Parameter group name since we need to tweak it later for installing pgAudit
Step 8: Configure logging
This is the important part
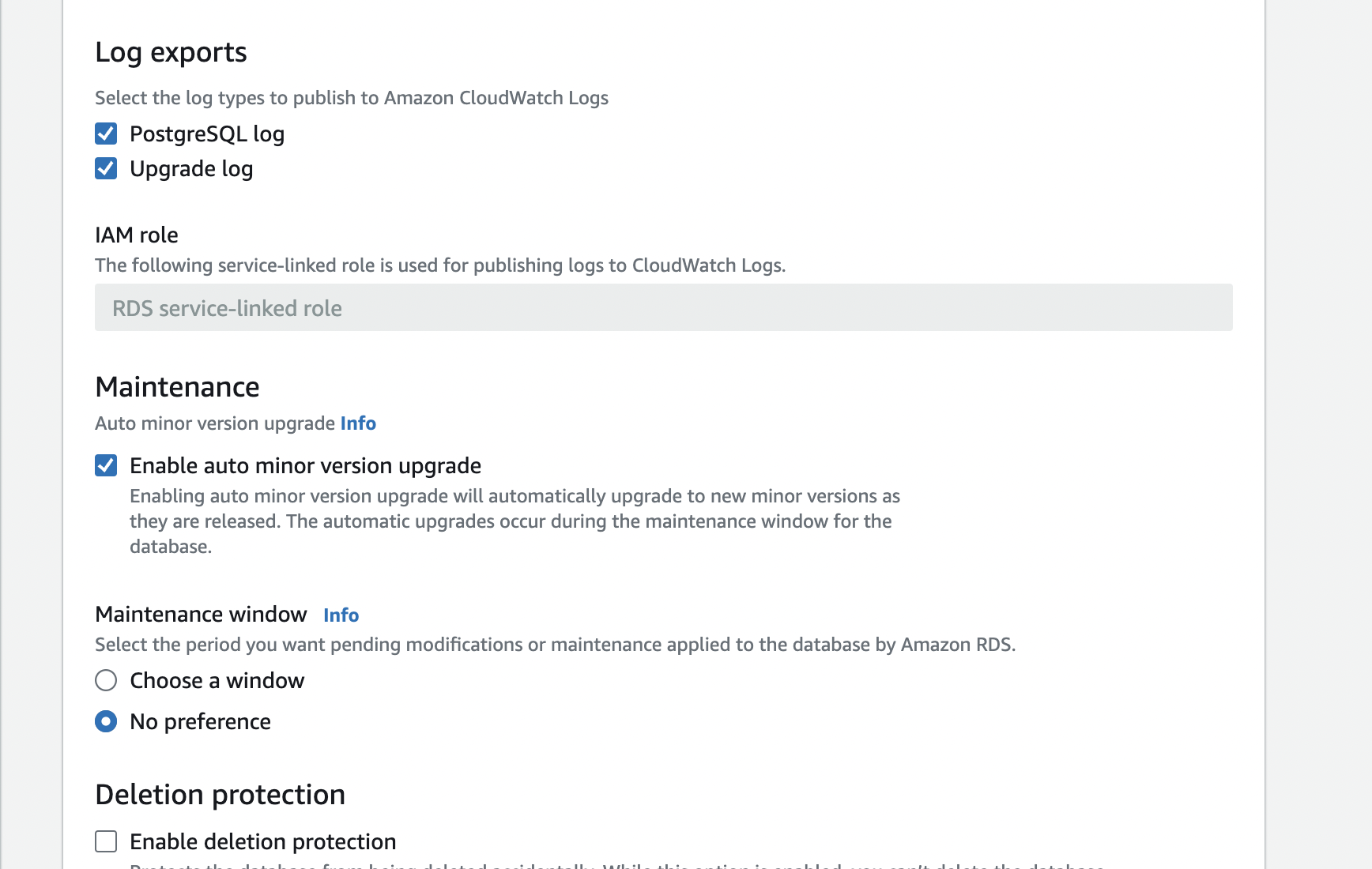
Configure log exports to Cloudwatch. Create a service linked role with necessary permissions if you haven’t. Give it admin access for now.
That’s it now click on “create database” and wait for the instance to be available
Step 9: Installing pgAudit
Follow this video for setting up your DB Parameter group, installing pgAudit and enabling it.
To load pgAudit, you need to configure the DB Parameter group to the following:
Set pgaudit.log to none, we’ll change this later from psql:
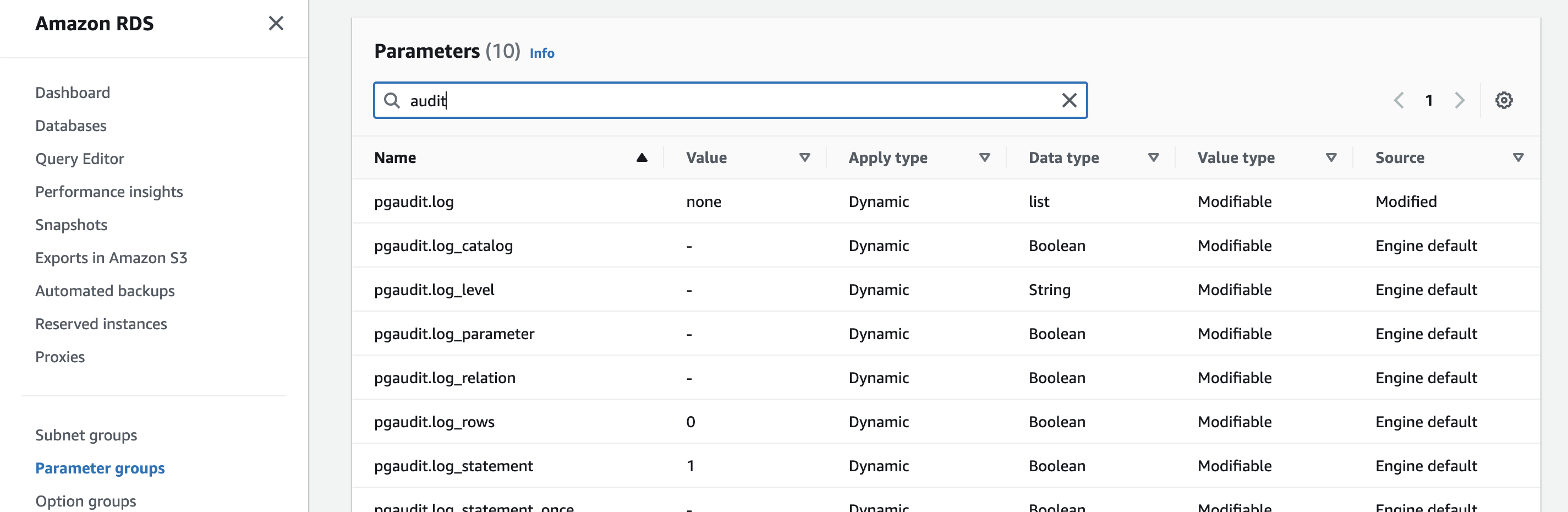
Load shared libraries via shared_preload_libraries:
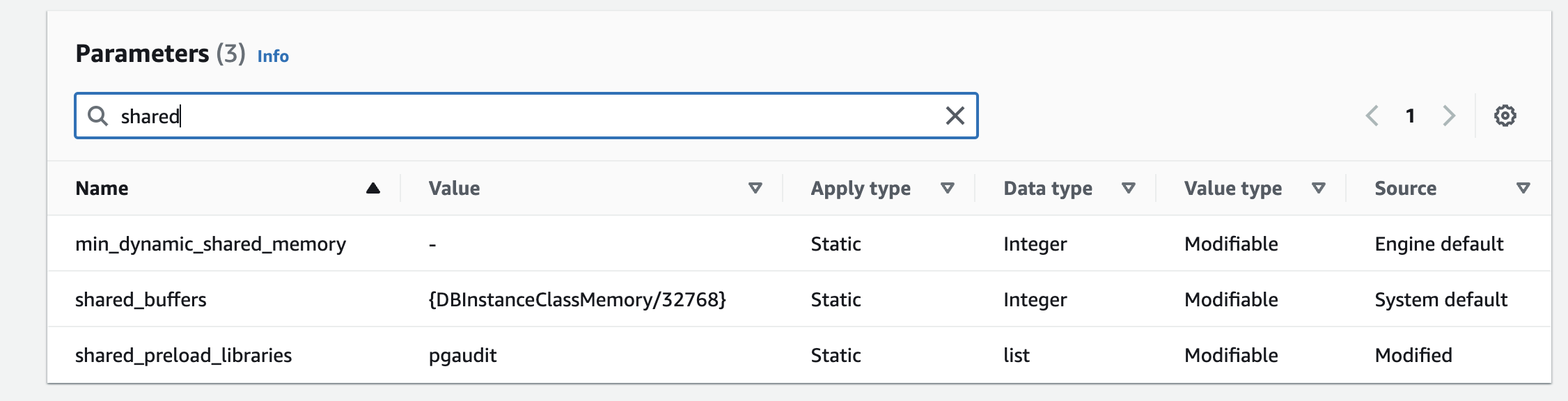
Set the pgaudot.role to the rds_pgaudit

Restart the instance and you should be able to use pgAudit
Log into your RDS using psql using
psql postgresql://postgres:password@small-sound.czei94v3hlkf.us-east-2.rds.amazonaws.com:5432/postgres
Then create a role for pgAudit
postgres=> CREATE ROLE rds_pgaudit; Check that the libraries are loaded
postgres=> show shared_preload_libraries;Then enable the extension
postgres=> CREATE EXTENSION pgaudit;Enable logs for pgAudit
For now, for testing purposes set log level to CREATE
postgres=> ALTER DATABASE test_database set pgaudit.log="CREATE"; But ideally, it should be
postgres=> ALTER DATABASE test_database set pgaudit.log="ALL"; Step 10: Testing that pgAudit works
In the psql shell
postgres=> CREATE TABLE test_table (id int);
postgres=> SELECT * FROM test_table;Go to logs & events tab
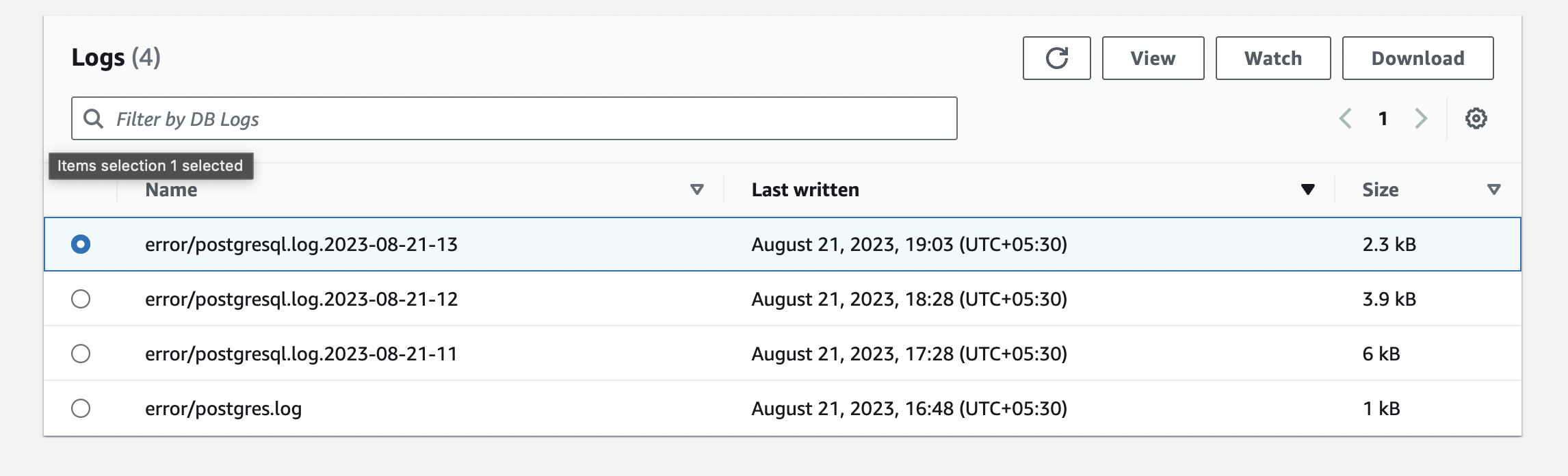
and check that the logs are reflected by clicking view on the latest written log file
Rocketgraph setup
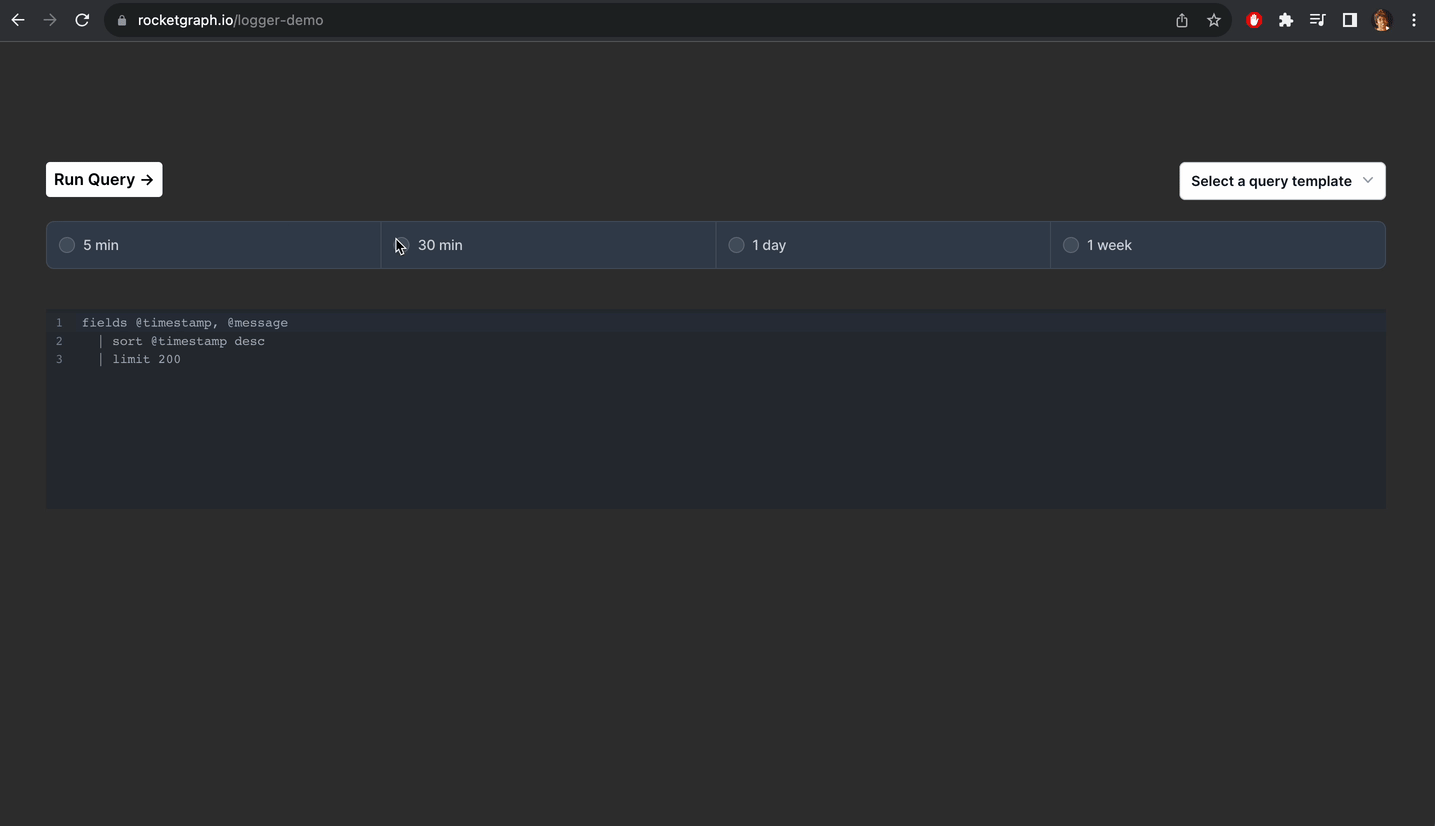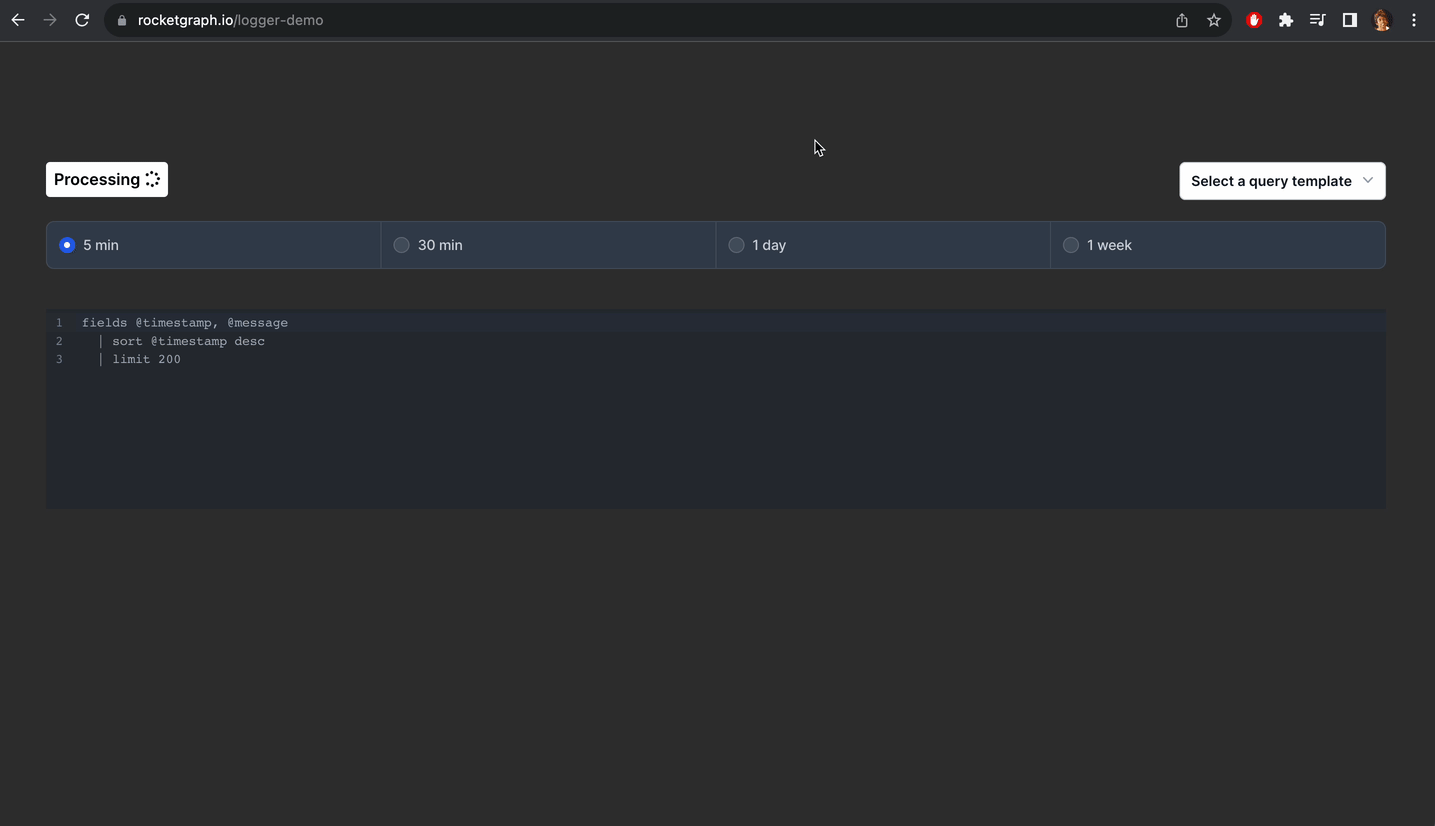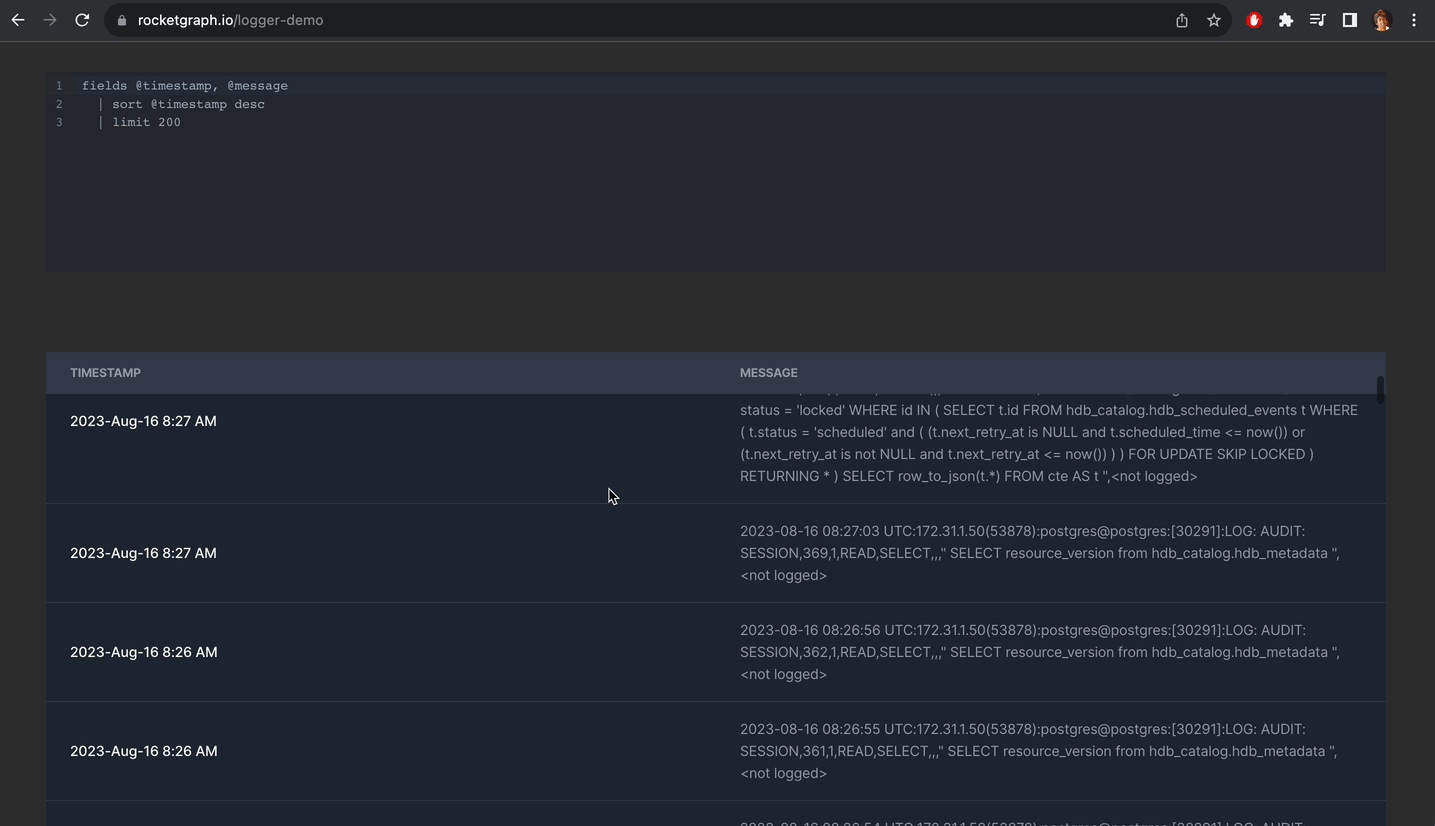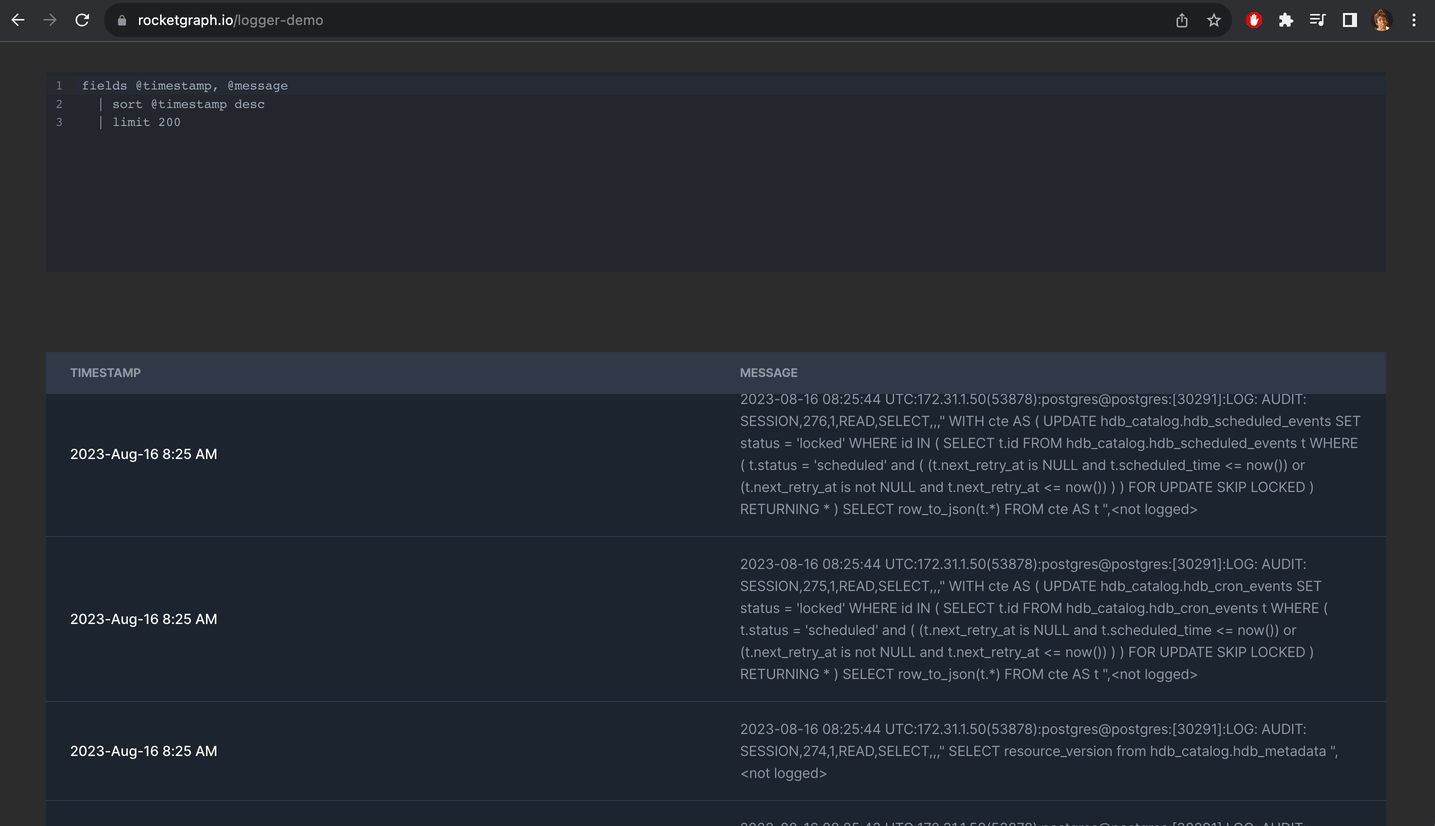
Alternatively you can create a project using Rocketgraph that comes with pgAudit enabled. You just need to do step 9. And once you create extension, you can see all your logs nicely like this:
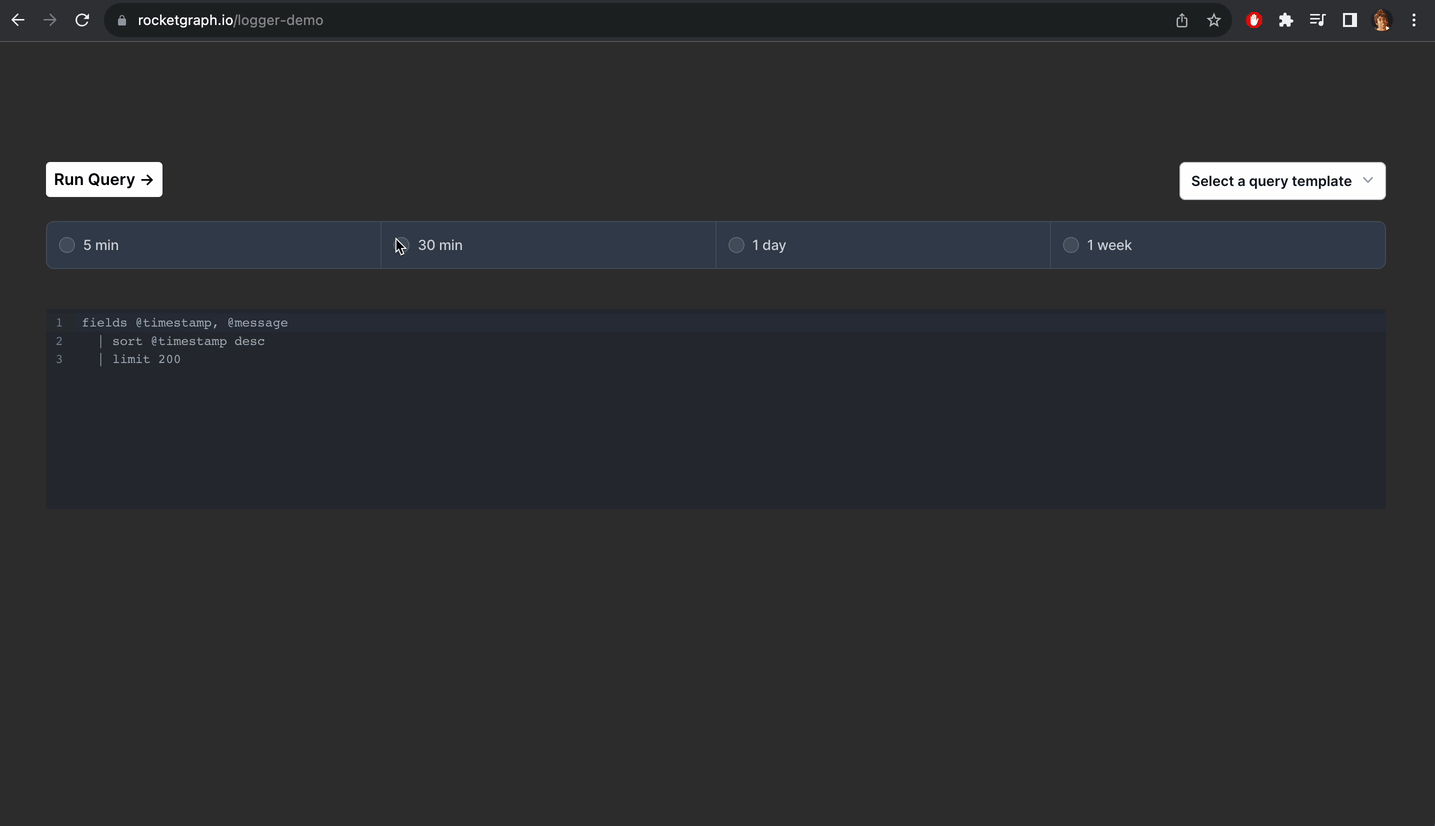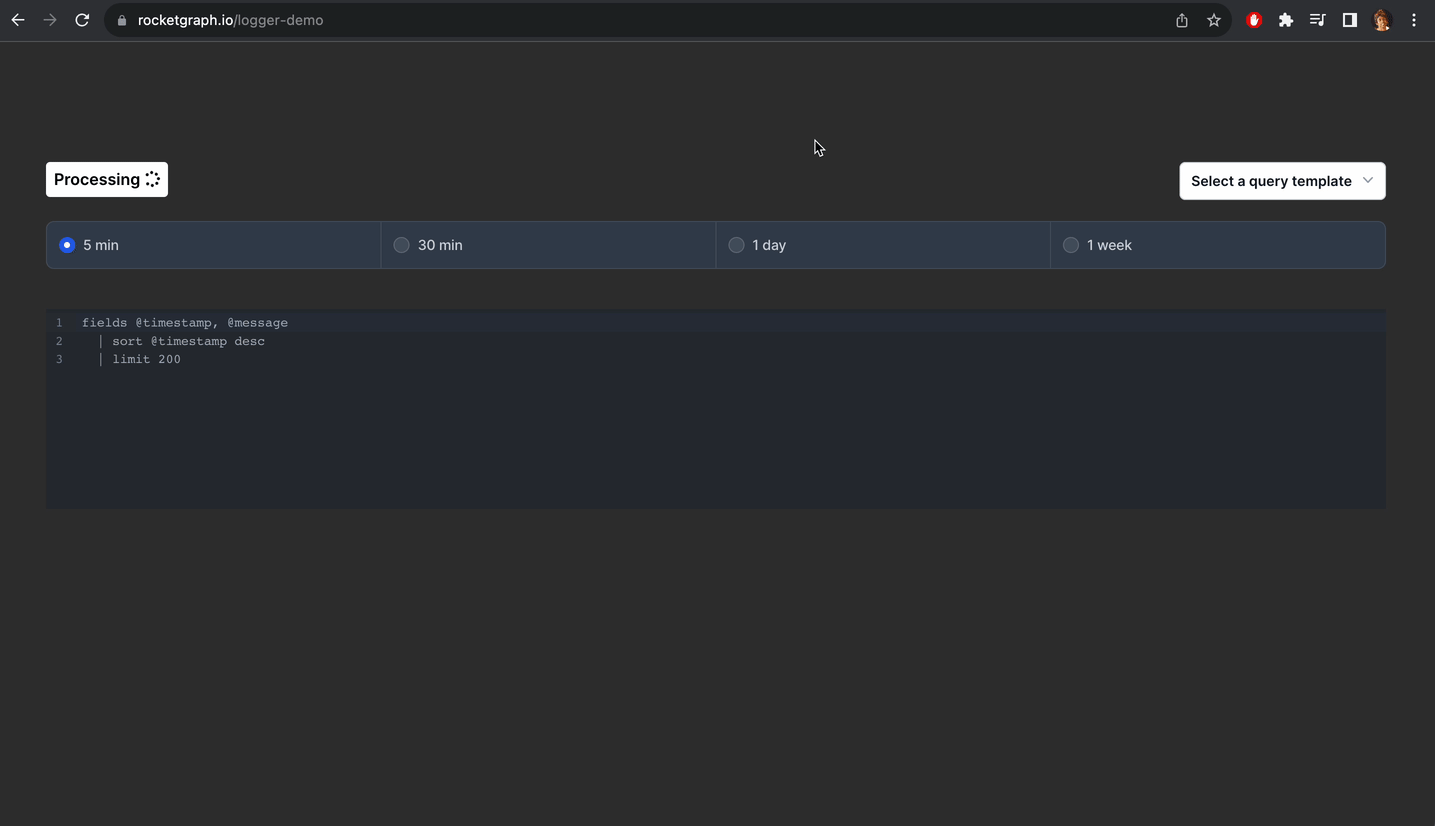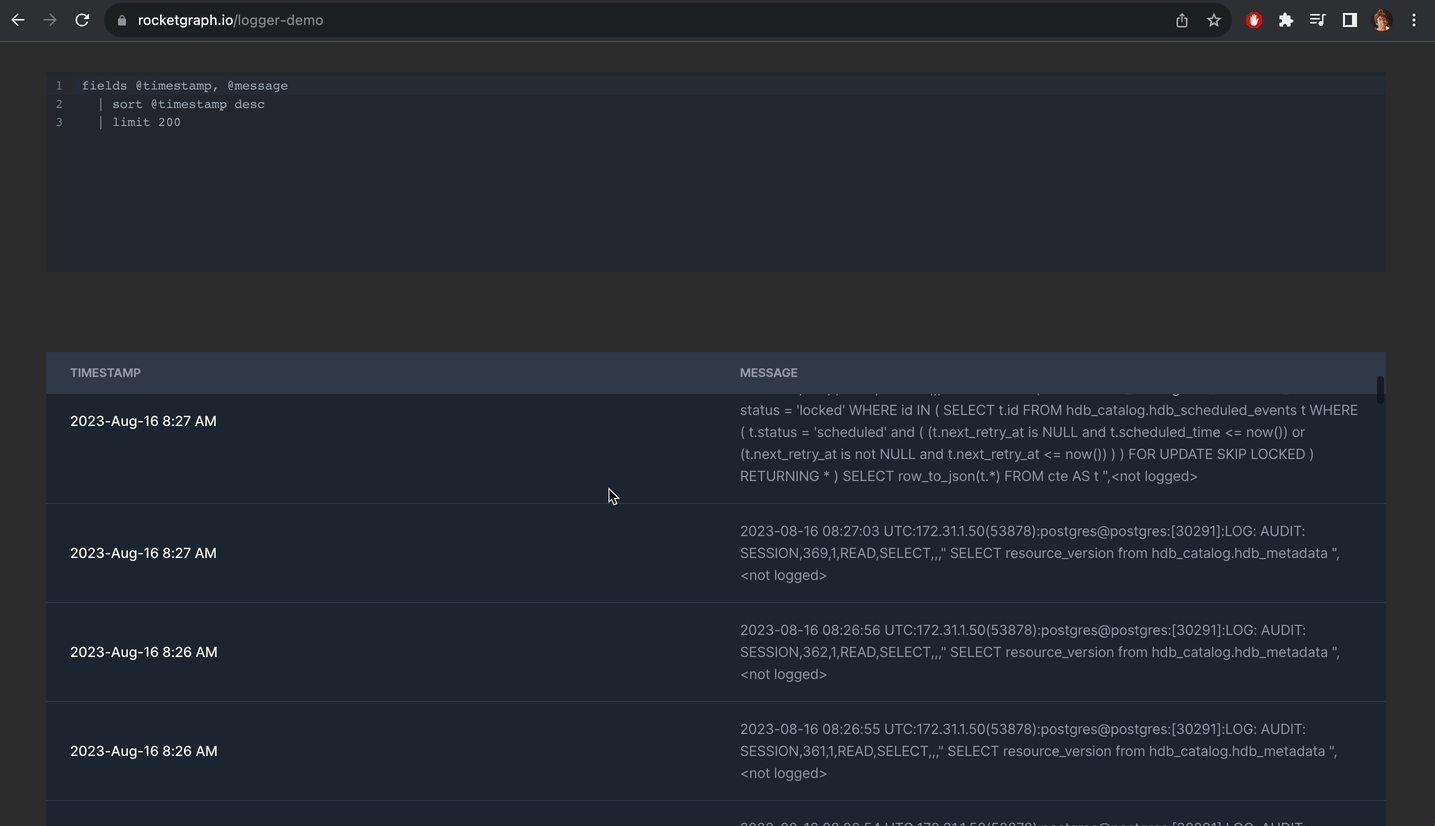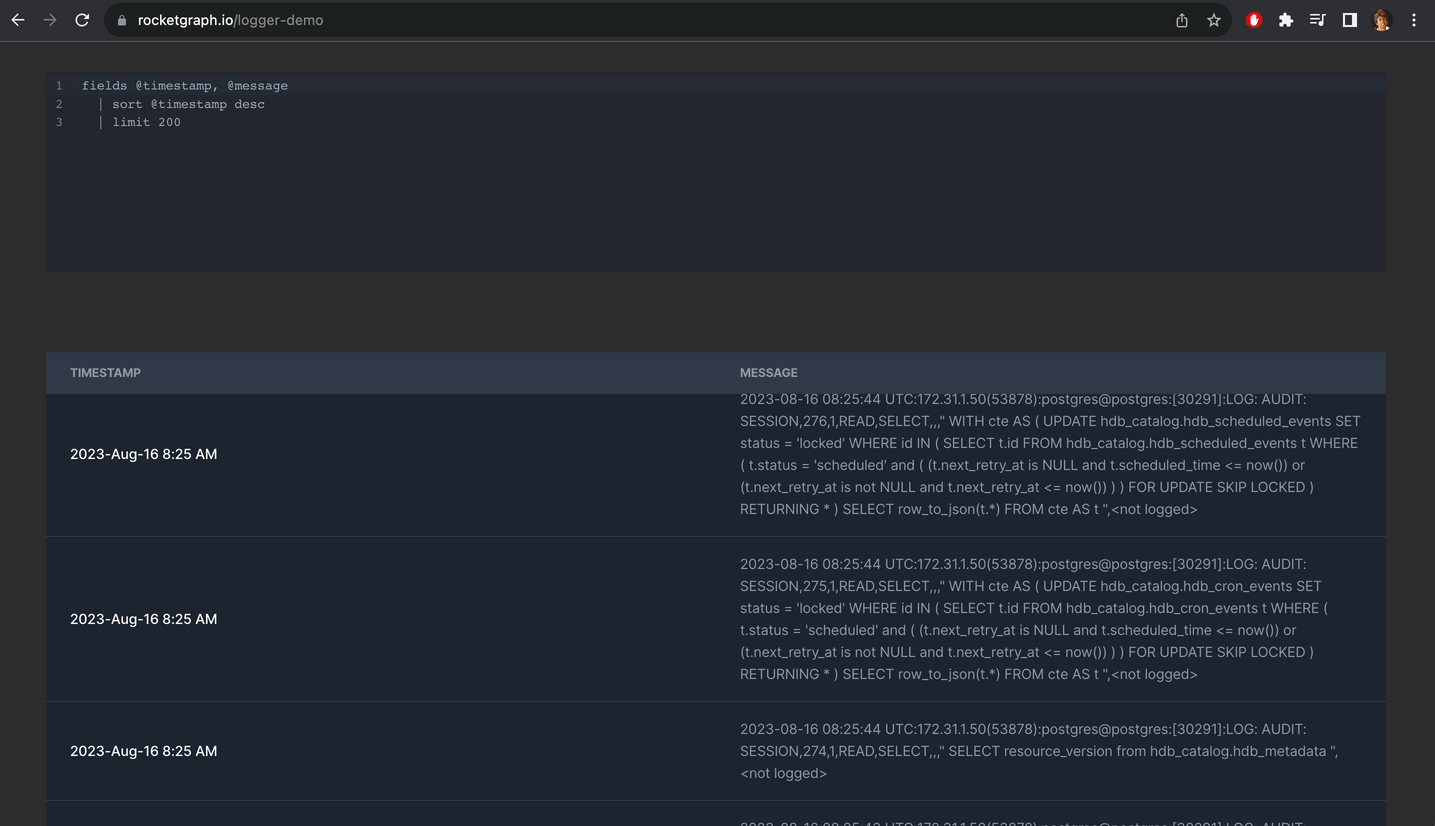
You can check out the demo here
